Mortality in Parkinsonã¢â‚¬â„¢s Disease a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstruse
Background
Trauma bloodshed in low- and eye-income countries (LMICs) remains loftier compared to high-income countries. Quality improvement processes, interventions, and structure are essential in the endeavour to subtract trauma bloodshed.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies assessing quality improvement processes, interventions, and construction in developing country trauma systems was conducted from November 1989 to August 2020 co-ordinate to the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Studies were included if they were conducted in an LMIC population co-ordinate to Earth Bank Income Classification, occurred in a trauma setting, and measured the effect of implementation and its impact. The primary outcome was trauma mortality.
Results
Of 37,575 search results, 30 studies were included from fifteen LMICs roofing five WHO regions in a qualitative synthesis. Twenty-seven articles were included in a meta-analysis. Implementing a pre-hospital trauma organisation reduced overall trauma mortality by 45% (risk ratio (RR) 0.55, 95% CI 0.4 to 0.75). Grooming kickoff responders resulted in an overall decrease in bloodshed (RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.78). In-hospital trauma preparation with certified courses resulted in a reduction of mortality (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.78). Trauma audits and trauma protocols resulted in varying improvements in trauma mortality.
Decision
In that location is testify that quality improvement processes, interventions, and structure tin ameliorate mortality in the trauma systems in LMICs.
Access options
Buy single commodity
Instant access to the full article PDF.
34,95 €
Price includes VAT (Indonesia)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
References
-
Reynolds TA, Stewart B, Drewett I, Salerno S, Sawe HR, Toroyan T et al (2017) The touch on of trauma care systems in low-and middle-income countries. Annu Rev Public Wellness 38:507–532
-
Gosselin RA, Spiegel DA, Coughlin R, Zirkle LG (2009) Injuries: the neglected brunt in developing countries. Bull World Wellness Organ 87:246
-
Mathers CD, Loncar D (2006) Projections of global mortality and brunt of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med 3(11):e442
-
Juillard CJ, Mock C, Goosen J, Joshipura M, Civil I (2009) Establishing the evidence base for trauma quality improvement: a collaborative WHO-IATSIC review. Earth J Surg 33(5):1075–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-009-9959-viii
-
Organization WH (2004) Guidelines for essential trauma intendance. World Wellness Organization, Geneva
-
Henry JA, Reingold AL (2012) Pre-hospital trauma systems reduce mortality in developing countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 73(ane):261–268
-
Schwarzer G (2007) meta: An R package for meta-analysis. R News vii(three):twoscore–45
-
Team RC. R: A language and environs for statistical calculating. 2013.
-
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan Grand et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355:i4919
-
Ali J, Adam RU, Gana TJ, Bedaysie H, Williams JI (1997) Result of the pre-hospital trauma life support plan (PHTLS) on pre-hospital trauma intendance. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 42(5):786–790
-
Arreola-Risa C, Mock C, Herrera-Escamilla AJ, Contreras I, Vargas J (2004) Cost-effectiveness and do good of alternatives to improve preparation for pre-hospital trauma care in Mexico. Pre-infirmary Disaster Med xix(4):318–325
-
Arreola-Risa C, Mock CN, Lojero-Wheatly L, De La Cruz O, Garcia C, Canavati-Ayub F et al (2000) Low-cost improvements in pre-hospital trauma care in a Latin American city. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 48(1):119–124
-
Husum H (1999) Effects of early pre-hospital life support to war injured: the boxing of Jalalabad, Afghanistan. Pre-hospital Disaster Med 14(2):43–48
-
Husum H, Gilbert Grand, Wisborg T, Van Heng Y, Murad M (2003) Rural pre-hospital trauma systems improve trauma issue in depression-income countries: A prospective study from Due north Iraq and Cambodia. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Intendance 54(half-dozen):1188–1196
-
Marson Air conditioning, Thomson JC (2001) The influence of pre-hospital trauma care on motor vehicle crash mortality. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 50(5):917–921
-
Murad MK, Issa DB, Mustafa FM, Hassan HO, Husum H (2012) Prehospital trauma system reduces mortality in severe trauma: A controlled study of road traffic casualties in Republic of iraq. Prehosp Disaster Med 27(ane):36–41
-
Nafissi N, Saghafinia M, Balochi G (2008) Improving trauma care in rural Iran by preparation existing treatment chains. Rural Remote Wellness 8(iv):881
-
Nia MS, Naffisi N, Mohebbi HA, Moharamzadeh Y (2008) The part of performing life support courses in rural areas in improving pre-infirmary physiologic weather of patients with penetrating injuries. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak xviii(9):538–541
-
Saghafinia Thou, Nafissi N, Asadollahi R (2009) Effect of the rural rescue system on reducing the mortality rate of landmine victims: a prospective study in Ilam Province, Iran. Pre-hospital Disaster Med 24(two):126–129
-
Wisborg T, Murad MK, Edvardsen O, Husum H (2008) Prehospital trauma system in a depression-income country: System maturation and accommodation during 8 years. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 64(5):1342–1348
-
Arreola-Risa C, Vargas J, Contreras I, Mock C (2007) Issue of emergency medical technician certification for all pre-hospital personnel in a Latin American city. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 63(iv):914–919
-
Husum H, Gilbert M, Wisborg T (2003) Training pre-hospital trauma care in low-income countries: the'Village University'experience. Med Teach 25(ii):142–148
-
Murad MK, Husum H (2010) Trained lay first responders reduce trauma mortality: a controlled study of rural trauma in Iraq. Pre-hospital Disaster Med 25(half dozen):533–539
-
Shi X-P, Qin L-J, Chang Y-10, Li F-L, Wang P (2019) Systemic analysis of pre-infirmary trauma emergency treatment in Zhengzhou. J Astute Dis eight(1):34
-
Ali J, Adam RU, Gana TJ, Bedaysie H, Williams JI (1997) Event of the pre-hospital trauma life support program (PHTLS) on pre-hospital trauma care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 42(5):786–790
-
Ariyanayagam DC, Naraynsingh 5, Maraj I (1992) The impact of the ATLS grade on traffic accident mortality in Trinidad and Tobago. West Indian Med J 41(ii):72–74
-
Cioè-Peña Eastward, Granados J, Wrightsmith Fifty, Henriquez-Vigil A, Moresky R (2017) Development and implementation of a hospital-based trauma response arrangement in an urban hospital in San Salvador. El salvador Trauma xix(2):118–126
-
Petroze RT, Byiringiro JC, Ntakiyiruta G, Briggs SM, Deckelbaum DL, Razek T et al (2015) Can focused trauma education initiatives reduce mortality or improve resource utilization in a depression-resource setting? World J Surg 39(iv):926–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2899-y
-
Schnittger T, Downie P, Pollach Thou (2011) The result of providing resuscitation grooming to forepart-line staff on rates of maternal and trauma mortality in ii wellness districts in Malawi. Malawi Med J 23(1):11–15
-
Van Heng Y, Davoung C, Husum H (2008) Non-doctors as trauma surgeons? A controlled study of trauma preparation for non-graduate surgeons in rural Kingdom of cambodia. Prehosp Disaster Med. 23(vi):483–489 (give-and-take 90-ane)
-
Wang P, Li North-P, Gu Y-F, Lu X-B, Cong J-Due north, Xin Y et al (2010) Comparison of severe trauma care effect before and after advanced trauma life support training. Chin J Traumatol (English language Edition). 13(6):341–344
-
Kaweesak Chittawatanarat MD, Ditsatham C, Kamtone Chandacham Doc, Tidarat Jirapongcharoenlap MD, Narain Chotirosniramit MD (2013) Effects of rapid response trauma team in thoracic injuries in northern trauma center level I. J Med Assoc Thai 96(ten):1319–1325
-
Erickson TB, VanRooyen MJ, Werbiski P, Mycyk M, Levy P (1996) Emergency medicine education intervention in Rwanda. Ann Emerg Med 28(6):648–651
-
Kesinger MR, Puyana JC, Rubiano AM (2014) Improving trauma care in depression- and middle-income countries past implementing a standardized trauma protocol. World J Surg 38(viii):1869–1874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2534-y
-
Mullan PC, Torrey SB, Chandra A, Caruso North, Kestler A (2014) Reduced overtriage and undertriage with a new triage system in an urban blow and emergency department in Botswana: a accomplice study. Emerg Med J 31(v):356–360
-
Chadbunchachai W, Saranrittichai S, Sriwiwat Due south, Chumsri J, Kulleab Due south, Jaikwang P (2003) Study on performance following Key Performance Indicators for trauma intendance: Khon Kaen Hospital 2000. J Med Assoc Thai 86(1):1–7
-
Chadbunchachai W, Sriwiwat S, Kulleab Due south, Saranrittichai S, Chumsri J, Jaikwang P (2001) The comparative study for quality of trauma treatment before and after the revision of trauma audit filter, Khon Kaen infirmary 1998. J Med Assoc Thai 84(6):782–790
-
Hashmi ZG, Haider AH, Zafar SN, Kisat M, Moosa A, Siddiqui F et al (2013) Hospital-based trauma quality improvement initiatives: offset step toward improving trauma outcomes in the developing earth. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 75(i):60–68 (discussion 8)
-
Moore L, Champion H, Tardif P-A, Kuimi B-50, O'Reilly Grand, Leppaniemi A et al (2018) Impact of trauma organization structure on injury outcomes: a systematic review and meta-assay. World J Surg 42(5):1327–1339. https://doi.org/x.1007/s00268-017-4292-0
-
Meara JG, Greenberg SL (2015) The Lancet Committee on Global Surgery Global surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare and economic development. Surgery 157(v):834–835
-
Kurdin A, Caines A, Boone D, Furey A (2018) Squad: a low-price culling to ATLS for providing trauma care pedagogy in Haiti. J Surg Educ 75(2):377–382
-
South SD, Boeck MA, Foianini JE, Swaroop Thou (2017) Advanced Trauma Life Support Preparatory Courses in Low-and Center-Income Countries. J Am Coll Surg 225(4):S98
-
Goosen J, Morris P, Kobusingye O, Mock C (2006) Advancing Essential Trauma Care through the partner organizations: IATSIC, ISS-SIC, and WHO. World J Surg 30(6):940–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0767-5
-
Stelfox HT, Joshipura Thousand, Chadbunchachai Westward, Ellawala RN, O'Reilly G, Nguyen TS et al (2012) Trauma quality comeback in low and middle income countries of the Asia-Pacific region: a mixed methods report. Earth J Surg 36(viii):1978–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1593-1
-
Mock C (2004) Guidelines for essential trauma care. World Health System, Geneva
-
Rosenkrantz L, Schuurman N, Arenas C, Nicol A, Hameed MS (2020) Maximizing the potential of trauma registries in low-income and middle-income countries. Trauma Surgery & Acute Care Open 5(one):e000469
-
Bommakanti K, Feldhaus I, Motwani Chiliad, Dicker RA, Juillard C (2018) Trauma registry implementation in low-and middle-income countries: challenges and opportunities. J Surg Res 223:72–86
Funding
At that place is no source of funding for this report.
Author information
Affiliations
Consortia
The International Society of Surgery (ISS) and the G4 Brotherhood International Standards and Guidelines for Quality Safe Surgery and Anesthesia (ISG-QSSA) Group
Corresponding writer
Ethics declarations
Disharmonize of interest
The authors declare that they accept no conflicts of interest.
Additional data
Publisher'southward Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix i: PRISMA-P (preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols) 2015 protocol
| Section and topic | Item No | Checklist detail |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative data | ||
| Championship | ||
| Identification | 1a | This report is a systematic review protocol |
| Update | 1b | No updated available |
| Registration | 2 | This systematic review is non registered with a database |
| Authors: | ||
| Contact | 3a | James Jin, corresponding author |
| Contributions | 3b | James Jin: database searching, screening of results, data extraction, data analysis, write up of manuscript and editing Salesi 'Akau'ola: 2d reviewer for screening of results Cheng-Har Yip: review of manuscript, data validation and assay, conceptualization of ideas Peter Nthumba: review of manuscript, data validation and assay, conceptualization of ideas Emmanuel A. Ameh: review of manuscript, data validation and assay, conceptualization of ideas Stijn de Jonge: review of manuscript, data analysis, conceptualization of ideas Mira Mehes: review of manuscript, conceptualization of ideas Iferemi Waiqanabete: review of manuscript, conceptualization of ideas Jaymie Henry: review of manuscript, data extraction, data validation and analysis, conceptualization of ideas Andrew Colina: review of manuscript, data validation and assay conceptualization of ideas |
| Amendments | 4 | No amendments |
| Support: | ||
| Sources | 5a | No fiscal support |
| Sponsor | 5b | No sponsor |
| Function of sponsor or funder | 5c | No role of funder or sponsor |
| Introduction | ||
| Rationale | vi | The Lancet Commission has highlighted inequity in the burden of surgical weather condition in LMICs compared to loftier-income countries. Morbidity and mortality statistics in LMIC further highlight the disparity. Quality improvement processes are integral in reducing morbidity and bloodshed in trauma systems. In that location is limited cognition on the effectiveness of such interventions in LMIC. We aimed to establish an evidence base for quality comeback interventions in trauma systems in LMIC that take a clear outcome on mortality |
| Objectives | seven | Research question: What are quality improvement processes, interventions and structure of trauma systems in low- and middle-income settings that can improve trauma mortality? Population: Low- and middle-income countries according to World Bank criteria. All study settings must include a low- or middle-income setting. We volition classify the setting co-ordinate to country, if the study takes place in a unmarried-center or multi-heart, and level of setting, i.eastward., urban or rural, primary vs 3rd, etc. Intervention: Interventions, construction, processes that improve morbidity and mortality in the above settings. These are specific interventions which have been implemented, and the effect of the implementation measured i.eastward., implementation of a checklist, guideline or construction which shows an comeback in morbidity or bloodshed Comparator: Comparator is the not-exposed control group; this includes study population before intervention Consequence: Morbidity and mortality measures |
| Methods | ||
| Eligibility criteria | eight | Studies to be included: Studies that satisfy the PICO criteria as in a higher place Studies that testify the consequence of a specific process, structure, or intervention on morbidity or mortality in trauma care systems, in a low–center-income-country setting Studies to be excluded are: 1. Studies not on trauma systems 2. Studies that practice not mention the implementation of a specific process, construction, or intervention 3. Studies that do non written report information on mortality 4. Studies that do not involve a low–centre-income-country setting Years to be considered- 1989, concluding search of database on August 18, 2020 Studies in English language But full-text studies are included |
| Information sources | 9 | MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane controlled register of clinical trials (CENTRAL), CINAHL, Scopus, WHO regional databases- Africa and Asia, Grey Literature, Open Grey Concluding search of database on August 13, 2020 |
| Search strategy | 10 | See Appendix |
| Study records: | ||
| Data management | 11a | Studies are imported into Endnote for screening and review |
| Pick process | 11b | At least two contained reviewers will screen the titles and abstracts using the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. If there are any disagreements, the titles and abstracts will be assessed by agreement |
| Information collection process | 11c | Data volition be obtained from reviewing the full-text paper. The information extraction table will be fabricated on Microsoft Excel The reviewers volition then add the relevant data to the tables |
| Data items | 12 | Pct reduction in mortality, risk ratio, report characteristics, number of participants, state, elapsing of study |
| Outcomes and prioritization | 13 | Percentage reduction in mortality, take chances ratio Additional outcome is cost-effectiveness. Cost of interventions measured in dollar amount if appropriate |
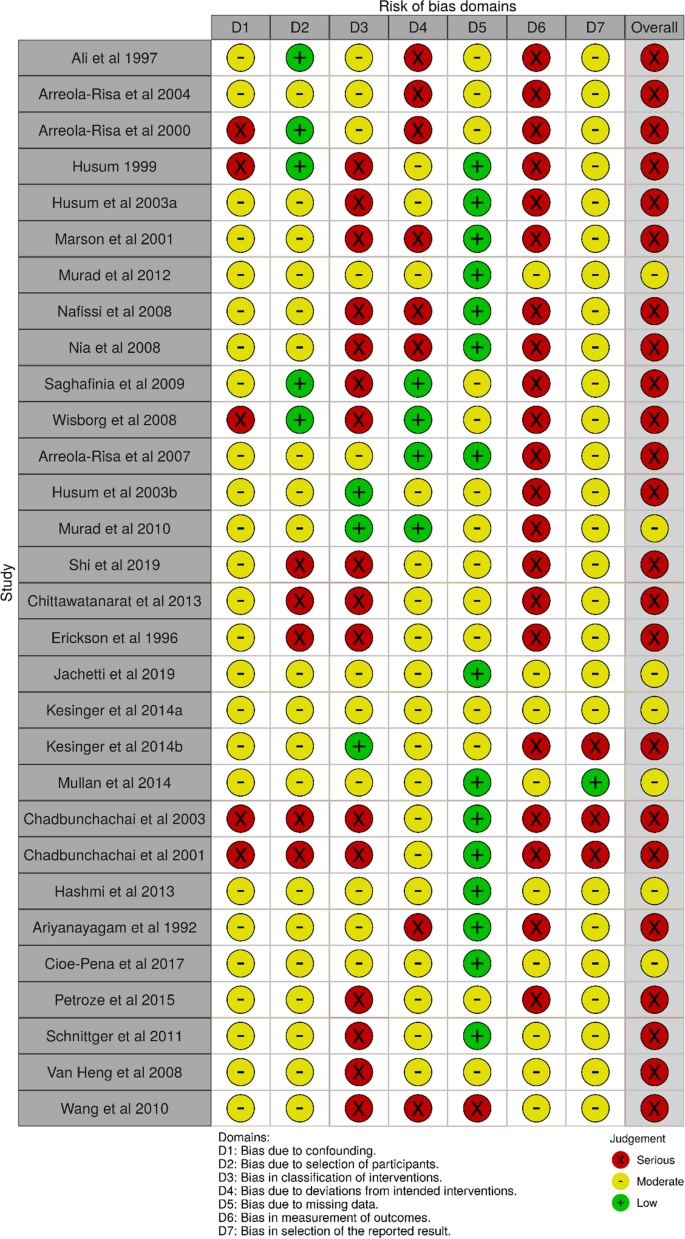
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 14 | Risk of bias analyzed for individual studies using the ROBBINS-I for observational studies and ROB 2.0 for randomized studies |
| Data synthesis | 15a | Information will be synthesized if the studies in question describes a similar intervention of a quality improvement intervention, structure or process |
| 15b | Meta-analysis will be conducted when the interventions and outcomes were determined to be combinable. Meta-analysis will be performed using appropriate software. The relative risk (RR, 95% conviction interval [CI]) of the primary event mortality using original data from the studies was calculated by dividing the cumulative incidence of bloodshed given the presence of an intervention by the cumulative incidence of mortality given the absence of an intervention. Relative risks greater than 1 signified an increased adventure of bloodshed in the presence of an intervention, whereas less than 1 signified a reduction of mortality of the given intervention. The Mantel–Haenszel method will exist used as the weighing method beyond studies. The upshot size called was the take a chance ratio RR. Random effects volition be called equally the analysis moderator. A funnel plot will be used to appraise the publication bias. Heterogeneity volition be measured using the I2 ¬statistic | |
| 15c | No sensitivity analyses volition be undertaken | |
| 15d | Nosotros will summarize the nature and the relative outcome of the interventions if the intervention cannot exist quantitatively synthesized | |
| Meta-bias(es) | 16 | Meta-biases volition be assessed at the individual study level using Cochrane Run a risk of bias tool |
| Conviction in cumulative evidence | 17 | We will non further synthesize the forcefulness of the body of prove in this review. A subsequent publication will exist published with Form findings |
From: Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew 1000, Shekelle P, Stewart L, PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-assay protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and caption. BMJ. 2015 Jan two;349(jan02 1):g7647.
Search strategy
Ovid MEDLINE(R) Epub Ahead of Print, In Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE (R) Daily, and Ovid MEDLINE (R) 1946-Present.
Embase <1980 to 2020 August xviii>
ane. Global Health/ or Developing Countries/ or Poverty/ 135032
2 (("low-and-middle-income" or "third-world" or "3rd earth" or developing or underdeveloped or "under-developed" or "less-developed" or "least-adult") adj3 (countr* or nation* or state* or region* or world*)).ti,ab,kw. 126258
3. ("low-and-middle-income" or "tertiary-world" or "3rd world" or "developing countr*" or "developing nation*" or "developing state*" or "developing region*" or "underdeveloped countr*" or "underdeveloped nation*" or "underdeveloped state*" or "underdeveloped region*" or "under- adult countr*" or "under-developed nation*" or "under-developed state*" or "under- developed region*" or "less-developed countr*" or "less-developed nation*" or "less-developed state*" or "less-developed region*" or "least-developed countr*" or "least-adult nation*" or "to the lowest degree-developed state*" or "least-developed region*").kw. 9314
four. LMIC*.ti,ab,kw. 6981
five. exp Afghanistan/ or exp Albania/ or exp Algeria/ or exp American Samoa/ or exp Angola/ or exp Argentina/ or exp Armenia/ or exp Azerbaijan/ or exp Bangladesh/ or exp Belarus/ or exp Belize/ or exp Benin/ or exp Bhutan/ or exp Bolivia/ or exp "Bosnia and Herzegovina"/ or exp Republic of botswana/ or exp Brazil/ or exp Bulgaria/ or exp Burkina Faso/ or exp Burundi/ or exp Cabo Verde/ or exp Kingdom of cambodia/ or exp Cameroon/ or exp Central African Republic/ or exp Chad/ or exp China/ or exp Republic of colombia/ or exp Comoros/ or exp "Democratic Congo-brazzaville"/ or exp Congo/ or exp Costa rica/ or exp Cote d'Ivoire/ or exp Republic of cuba/ or exp Djibouti/ or exp Dominica/ or exp Dominican Republic/ or exp Ecuador/ or exp Egypt/ or exp El Salvador/ or exp Equatorial Guinea/ or exp Eritrea/ or exp Ethiopia/ or exp Fiji/ or exp Gabon/ or exp Gambia/ or exp "Georgia (Democracy)"/ or exp Ghana/ or exp Grenada/ or exp Guatemala/ or exp Republic of guinea/ or exp Guinea-bissau/ or exp Guyana/ or exp Republic of haiti/ or exp Republic of honduras/ 562736
6. exp Bharat/ or exp Indonesia/ or exp Islamic republic of iran/ or exp Iraq/ or exp Jamaica/ or exp Jordan/ or exp Kazakhstan/ or exp Kenya/ or exp Republic of kiribati/ or exp "Democratic people's republic of korea"/ or exp Kosovo/ or exp Kyrgyzstan/ or exp Laos/ or exp Lebanon/ or exp Kingdom of lesotho/ or exp Liberia/ or exp Libya/ or exp Republic of madagascar/ or exp Malawi/ or exp Malaysia/ or exp Maldives/ or exp Mali/ or exp Republic of the marshall islands/ or exp Mauritania/ or exp Mauritius/ or exp United mexican states/ or exp Micronesia/ or exp Moldova/ or exp Mongolia/ or exp Montenegro/ or exp Morocco/ or exp Mozambique/ or exp Myanmar/ or exp Namibia/ or exp Republic of nauru/ or exp Nepal/ or exp Nicaragua/ or exp Niger/ or exp Nigeria/ or exp "Macedonia (Republic)"/ or exp Islamic republic of pakistan/ or exp Papua New Guinea/ or exp Paraguay/ or exp Peru/ or exp Philippines/ 474983
7. exp Romania/ or exp Russia/ or exp Rwanda/ or exp Samoa/ or exp "Independent State of Samoa"/ or American Samoa/ or Samoa/ or exp "Sao Tome and Principe"/ or exp Senegal/ or exp Serbia/ or exp Sierra Leone/ or exp Solomon Islands/ or exp Somalia/ or exp South Africa/ or exp South Sudan/ or exp Sri Lanka/ or exp Saint Lucia/ or exp "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines"/ or exp Sudan/ or exp Suriname/ or exp Syria/ or exp Tajikistan/ or exp Tanzania/ or exp Thailand/ or exp Timor-Leste/ or exp Togo/ or exp Tonga/ or exp Tunisia/ or exp Turkey/ or exp Turkmenistan/ or exp Tuvalu/ or exp Uganda/ or exp Ukraine/ or exp Uzbekistan/ or exp Vanuatu/ or exp Venezuela/ or exp Vietnam/ or exp Republic of yemen/ or exp Republic of zambia/ or exp Zimbabwe/ 272953
8. (Afghanistan* or Albania* or Algeria* or "American Samoa*" or Angola* or Argentina* or Armenia* or Azerbaijan* or Bangladesh* or Belarus* or Belize* or Benin* or Bhutan* or Bolivia* or Bosnia* or Herzegovina* or Botswana* or Brazil* or Bulgaria* or "Burkina Faso*" or Burundi* or "Cabo Verde*" or Cambodia* or Republic of cameroon* or "Fundamental African Republic*" or Chad* or China* or Colombia* or Union of the comoros* or Congo* or "Republic of costa rica*" or "Republic of cote d'ivoire*" or "Ivory Coast*" or Republic of cuba* or Djibouti* or Dominica* or "Dominican Commonwealth*" or Ecuador* or Egypt* or "El Salvador*" or "Republic of equatorial guinea*" or Eritrea* or Ethiopia* or Fiji* or Gabon* or Gambia* or Georgia* or Ghana* or Grenada* or Guatemala* or Republic of guinea* or "Republic of guinea-bissau*" or Guyana* or Haiti* or Honduras*).ti,ab,kw. 734873
ix. (India* or Indonesia* or Iran* or Republic of iraq* or Jamaica* or Jordan* or Republic of kazakhstan* or Kenya* or Kiribati* or Korea* or Kosovo* or Kyrgyzstan* or Laos* or Lebanon* or Lesotho* or Republic of liberia* or Libya* or Republic of madagascar* or Republic of malaŵi* or Malaysia* or Maldives* or Republic of mali* or "Marshall Islands*" or Mauritania* or Mauritius* or Mexico* or Micronesia* or "Micro-nesia*" or Moldova* or Mongolia* or Montenegro* or Kingdom of morocco* or Mozambique* or Myanmar* or Namibia* or Nauru* or Nepal* or Nicaragua* or Niger* or Nigeria* or Macedonia* or Pakistan* or "Papua New Republic of guinea*" or Paraguay* or Peru* or Philippines*).ti,ab,kw. 1552235
ten. (Romania* or Russia* or Rwanda* or Samoa* or "Sao Tome*" or Principe* or Senegal* or Serbia* or "Sierra Leone*" or "Solomon Islands*" or Somalia* or "South Africa*" or Sudan* or "Sri Lanka*" or "Saint Lucia*" or "St Lucia*" or "Saint Vincent*" or "St Vincent*" or Grenadines* or Suriname* or Syrian arab republic* or Tajikistan* or Tanzania* or Thailand* or "Timor-Leste*" or Togo* or Tonga* or Tunisia* or Turkey* or Turkmenistan* or Tuvalu* or Uganda* or Ukraine* or Uzbekistan* or Vanuatu* or Venezuela* or Vietnam* or Yemen* or Zambia* or Zimbabwe*).ti,ab,kw. 346401
11. surg*.mp. [mp = title, abstruse, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading discussion, candidate term word] 4095718
12. trauma.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term word] 336005
13. quality improvement.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device merchandise name, keyword, floating subheading discussion, candidate term give-and-take] 63546
14. intervention.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading give-and-take, drug trade name, original championship, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device merchandise proper noun, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term word] 1008372
15. protocol*.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading give-and-take, drug merchandise proper name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading give-and-take, candidate term discussion] 746447
xvi. guideline*.mp. [mp = championship, abstract, heading give-and-take, drug merchandise name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading give-and-take, candidate term discussion] 791948
17. checklist*.mp. [mp = championship, abstract, heading word, drug trade proper name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device merchandise name, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term discussion] 64328
18. safe*.mp. [mp = championship, abstruse, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term word] 1650025
19. exp morbidity/ or exp basic reproduction number/ or exp mortality/ or exp "cause of death"/ or exp child bloodshed/ or exp fatal event/ or exp fetal mortality/ or exp hospital mortality/ or exp infant mortality/ or exp maternal mortality/ or exp mortality, premature/ or exp survival charge per unit/ 1576337
20. bloodshed.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading discussion, drug trade proper name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term word] 1513865
21. morbidity.mp. [mp = title, abstruse, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term word] 680061
22. adverse event*.mp. [mp = title, abstract, heading word, drug trade proper name, original championship, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade proper noun, keyword, floating subheading word, candidate term give-and-take] 326054
23. one or two or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or viii or 9 or x 2904901
24. structure.mp. 2106950
25. 13 or fourteen or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 24 5827264
26. 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 2350970
27. 11 or 12 4296066
28. 23 and 25 and 26 and 27 25133
Appendix ii: Hazard of bias for individual studies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this commodity
Jin, J., Akau'ola, Due south., Yip, CH. et al. Effectiveness of Quality Improvement Processes, Interventions, and Construction in Trauma Systems in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-assay. Earth J Surg 45, 1982–1998 (2021). https://doi.org/x.1007/s00268-021-06065-9
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
Issue Engagement:
-
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-021-06065-ix
Source: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00268-021-06065-9
0 Response to "Mortality in Parkinsonã¢â‚¬â„¢s Disease a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis"
Post a Comment